A good estimate of your post-retirement income is essential for effective retirement planning. But gauging your income can be tricky when it comes from multiple sources. Fortunately, there are a variety of online calculators that can help you get started.

NYSLRS Benefit Calculator
Most NYSLRS members can quickly create a pension estimate using Retirement Online. Your estimate will be based on the most up-to-date account information we have on file for you. You can enter different retirement dates to see how those choices would affect your benefit and adjust your earnings or service credit if you anticipate a raise or plan to purchase past service.
Social Security Calculators
The Social Security Administration (SSA) hosts several calculators that you may find helpful. Their Quick Calculator uses information you enter to provide a rough Social Security benefit estimate. Their Retirement Estimator calculates your benefit based on your actual earnings. You’ll need to enter your Social Security number and other personal information to create an SSA account.
You can also look up when you will be eligible for full Social Security benefits and estimate your life expectancy.
Savings Calculators
If you are saving for retirement, a simple savings calculator can give you an idea of how your money can grow over the years. However, simple calculators like this assume a fixed amount of savings each month. Most people increase their retirement savings as their income grows.
If you have a 457(b) plan like those offered by the New York State Deferred Compensation Plan, you can use their interactive retirement planner to project a hypothetical view of what your retirement may look like based on information you provide
Savings Withdrawal Calculators
Savings withdrawal calculators are designed to help determine how much savings remains after a series of withdrawals. These are especially helpful tools to use when trying to determine how long your retirement savings will last, based on a starting amount, how much you expect to withdraw, how often and some other factors.
How Much Do You Need?
Now that you’ve estimated your potential sources of retirement income, it’s important to understand your anticipated expenses in retirement. Our Income and Expenses Worksheet can help you create a post-retirement budget.
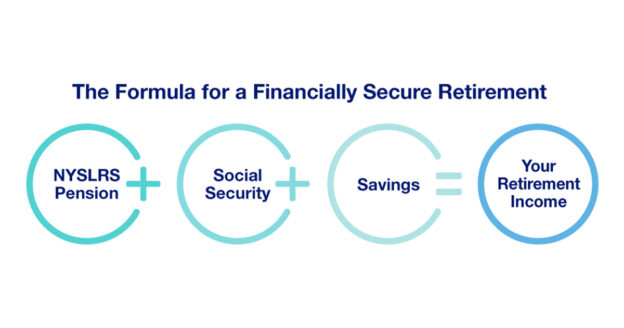
Think of retirement security as a three-legged stool, with your NYSLRS pension, social security benefit and retirement savings working together to provide financial stability. Your NYSLRS pension is a defined benefit, or traditional pension, that will provide you with a monthly payment for the rest of your life. Having a retirement savings account can give you more flexibility to do the things you want to do, or provide a source of cash in case of an emergency. Start saving for retirement if you haven’t already, or give your retirement savings a boost.